Fiber Optic
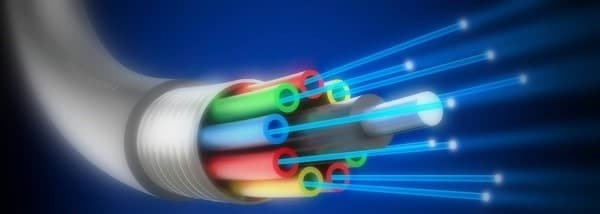
Fiber optics are a type of technology that transmits pulses in the form of filaments of glass or plastic.
The diameter of each optical fiber is like a human hair, if we put more optical fibers together, it transmits more information faster than any other tool and over longer distances.
Fiber optics consist of three parts
A: Core (Optical Filaments)
B: Coating: Glass layer around the core
A: The buffer pipe cover that protects the sheath and has an outer cover that protects the whole cable.
Fiber optic cable has more advantages than copper cables. These fibers are used in telecommunication services such as the Internet, television, and telephone.
For example, Google uses fiber optics in Google Fiber services and provides people with faster internet speeds.
History of Fiber Optic
In the late 1960s, Dr. Charles Cohen Cao and a colleague in the United Kingdom determined that these cables were not working properly because of the impurities in the glass of fiber optic cables at the time.
Early fiber optic cables, before all light was lost, could carry telephone and television signals for 65 feet through pulses of light. But in 1970, researchers created a pure optical fiber that was more than 2,640 feet long.
This optical fiber, which resembled a fishing rope, enabled higher bandwidth communication ranges. In 2009, it was estimated that the number of fiber optic cables used worldwide would form a strand of more than 600 million miles long if interconnected.
Performance of optical fibers
Optical fibers work with the principle of general internal reflection and light beams are used to transmit data, but the problem is that if the long wire is curved, the light beams cannot move and only move directly.
Types of Fiber Optic Cable
-
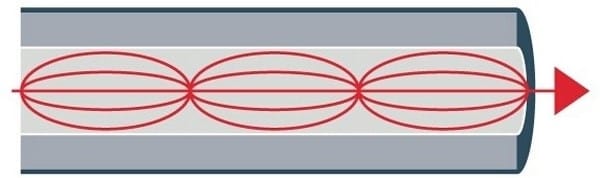
Single-mode fiber:
Because of the smaller diameter of the glass fiber core, single-mode optical fibers are used for long distances. The smaller span of these cables isolates light into a single beam, providing a more direct path and enabling the signal to travel longer distances.
These fibers have a higher bandwidth than multimode fibers, and the light source of these fibers is laser.
The light source used for single-mode fiber is often laser. Single-mode fiber usually has a higher price.
-
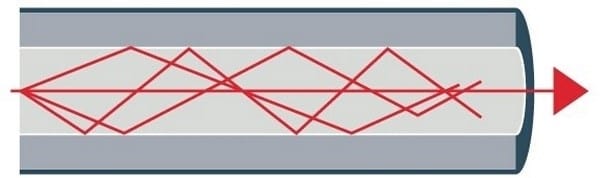
Multimode Fiber:
Multimode fiber is used for short distances. The larger opening of the nucleus of this fiber allows the signals to be reflected to a greater extent. Because the diameter of this multimode fiber is larger, several pulses of light are sent at the same time. Of course, there is a possibility of signal loss or interference.
-
Fiber Optic with Gradual Refractive Index:
Today, this type of optical fiber is the most widely used. In this fiber, the light that travels closer to the center is slower than the light that travels closer to the coating. Therefore, the classification of light rays is better, and in this case, the refractive index is reduced.
-
Fiber Optic with Stepwise Refractive Index:
This fiber moves light in different directions in a zigzag and straight way, and it is reflected from the coating. As a result, in all cases, the light reaches the end of the fiber.
Fiber Optic Components:
Fiber optics are made up of a variety of components and materials, often a combination of glass or plastic.
The benefits of fiber optics include:
Connection Quality
High Bandwidth
Ability to transmit signals over long distances
Small size
Light weight
Ability to easily increase bandwidth
High Security
Disadvantages of Fiber Optics:
Fragility
Difficult to install
Dispersion
Needing special equipment
Care of Optical Fibers:
This cable is not lost due to damage and breakage, however, it is possible to interrupt the signal due to contaminants and pollution and dust. Even a drop of oil can destroy this connection.